Introduction
The S&P 500 Index, or Standard & Poor's 500 Index, is a market-capitalization-weighted index of 500 leading U.S. companies, including 503 components due to some dual share classes. Beyond market cap, it uses various criteria for selection. As a premier gauge of American equities' performance, it reflects the health of the U.S. stock market, with a diverse composition chosen for industry representation, liquidity, and financial stability.
An S&P 500 Index ETF provides investors with a diverse portfolio without purchasing individual shares of the largest U.S. companies. It offers moderate risk and is less volatile than sector-specific ETFs like those in oil exploration or cryptocurrency. Investing in established companies reduces the likelihood of severe downturns. It mirrors the S&P 500, ideal for passive investors, offering broad market exposure to firms like Microsoft, Walmart, Coca-Cola, and Merck.
However, it is essential to have a certain level of understanding while investing in SP500 ETF, including the mechanics of investing in SP500 index ETF, opportunities, and risks. This article will introduce you to SP500 ETFs, the key factors when choosing any SP500 ETF, besides listing the top five SP500 ETFs, performance comparison, common myths, how to invest, and many more.
Understanding S&P 500 ETFs
What is an ETF?
An exchange-traded fund or ETF is a pooled investment asset or security that enables anyone to trade like any individual asset. ETFs can be crafted to follow anything from the price of a particular asset or commodity to a broad array of securities. They can also be tailored to specific investment strategies. Investors can access various ETFs for speculation, income generation, price appreciation, and risk hedging. The pioneering ETF was the SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY), designed to track the performance of the S&P 500 Index.
What is the SP500 index?
The Standard and Poor’s 500, or SP500, index is a stock market index that tracks the performance of the top 500 large publicly traded companies listed on the U.S. stock exchange. It was launched in 1957, and its author is the credit rating agency Standard and Poor's.
Indexes like the S&P 500 track the prices of a group of securities to represent the performance of specific markets, industries, economic segments, and even entire national economies. There are indexes for every asset class and business sector, from U.S. corporate bonds to palladium futures.
The S&P 500 tracks large-cap U.S. stocks or companies with market values exceeding $10 billion. By following the S&P 500, you can easily gauge the performance of America's largest stocks.
This is why the S&P 500 is often regarded as a proxy for the overall health of the stock market and the U.S. economy.
How SP500 ETFs work
First introduced in January 1993, SP500 ETF (SPY) was the first index ETF listed in the United States. Index ETFs are exchange-traded funds designed to track the benchmark index performance passively.
The S&P 500 Index is the benchmark for any SP500 ETF, meaning the managing institution buys stocks of all companies listed in the index, matching its weighting. Consequently, an investor's returns will increase or decline with the S&P 500.
However, this management is complex. The ETF manager must continually adjust the portfolio, buying or selling stocks to reflect index changes. Stocks may be removed due to mergers or failing to meet criteria. When changes occur, the ETF sponsor sells outgoing stocks and adds new listings. Buying SPY means taking a long position in the SP500, while selling SPY equates to a short position. Like individual stocks, SP500 ETFs also have associated options.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing S&P 500 ETFs
This part lists the significant factors to check while choosing SP500 ETFs to invest in.
Expense Ratio
The expense ratio is a crucial factor to consider when seeking potential SP500 ETFs. While both active and passive ETFs exist, most S&P 500 ETFs are passively managed. These ETFs rank among the largest by assets and have high trading volumes. Typically, they feature very low expense ratios to cover operating costs. If an S&P 500 ETF has a higher expense ratio, assessing whether the fund’s performance justifies the increased management fee is important.
Tracking Accuracy
Another mandatory factor in choosing SP500 ETFs is tracking accuracy or ensuring it accurately mirrors the SP500 index. It includes checking the fund’s tracking error which is the measurement between the funds and ETFs returns. A minor tracking error indicates better tracking accuracy. Consistently low tracking error over time suggests that the ETF efficiently replicates the index, providing alignment and reliable performance with the S&P 500's movements.
Liquidity
Another significant factor to consider when investing in SP500 ETF Hands-off is that retirement investors or long-term investors with a buy-and-hold strategy generally don't need to worry about ETF liquidity. However, active investors trading in taxable brokerage accounts should consider how an ETF’s liquidity may have impacted their investment strategy. More liquid funds have higher average trading volumes, making buying and selling shares promptly easier. Conversely, funds with lower trading volumes are less liquid. Selecting a more liquid S&P 500 fund ensures you can execute trades quickly without compromising returns.
Fund Size
Fund size is another important factor for investors seeking a potential SP500 ETF, as significant funds offer more liquidity and greater stability. Significant funds usually have significant trading volume, which makes it easier to trade without affecting the price. Moreover, larger funds enable having a lower expense ratio due to economic scale. A well-established, sizable fund with significant assets under management can provide more confidence in consistent performance and efficient tracking of the S&P 500 Index.
Historical Performance
Historical performance is another mandatory factor to check while selecting SP500 ETFs. Newer ETFs have shorter performance track records, which is significant for S&P 500 ETFs. Older funds have experienced more economic cycles and have been stress-tested in various market conditions. By reviewing the performance history of older funds, investors can gain more confidence in predicting how a fund might perform in future cycles. This historical perspective helps assess the fund’s resilience and potential stability in diverse economic environments.
Best S&P 500 ETFs
Today there is a significant number of ETFs available to invest. So, selecting the most promising or potential SP 500 ETFs among the rapidly developing basket of ETFs is an underappreciated challenge. This part briefly introduces the top potential SP500 ETFs, depending on key factors.
SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust (SPY)
Overview
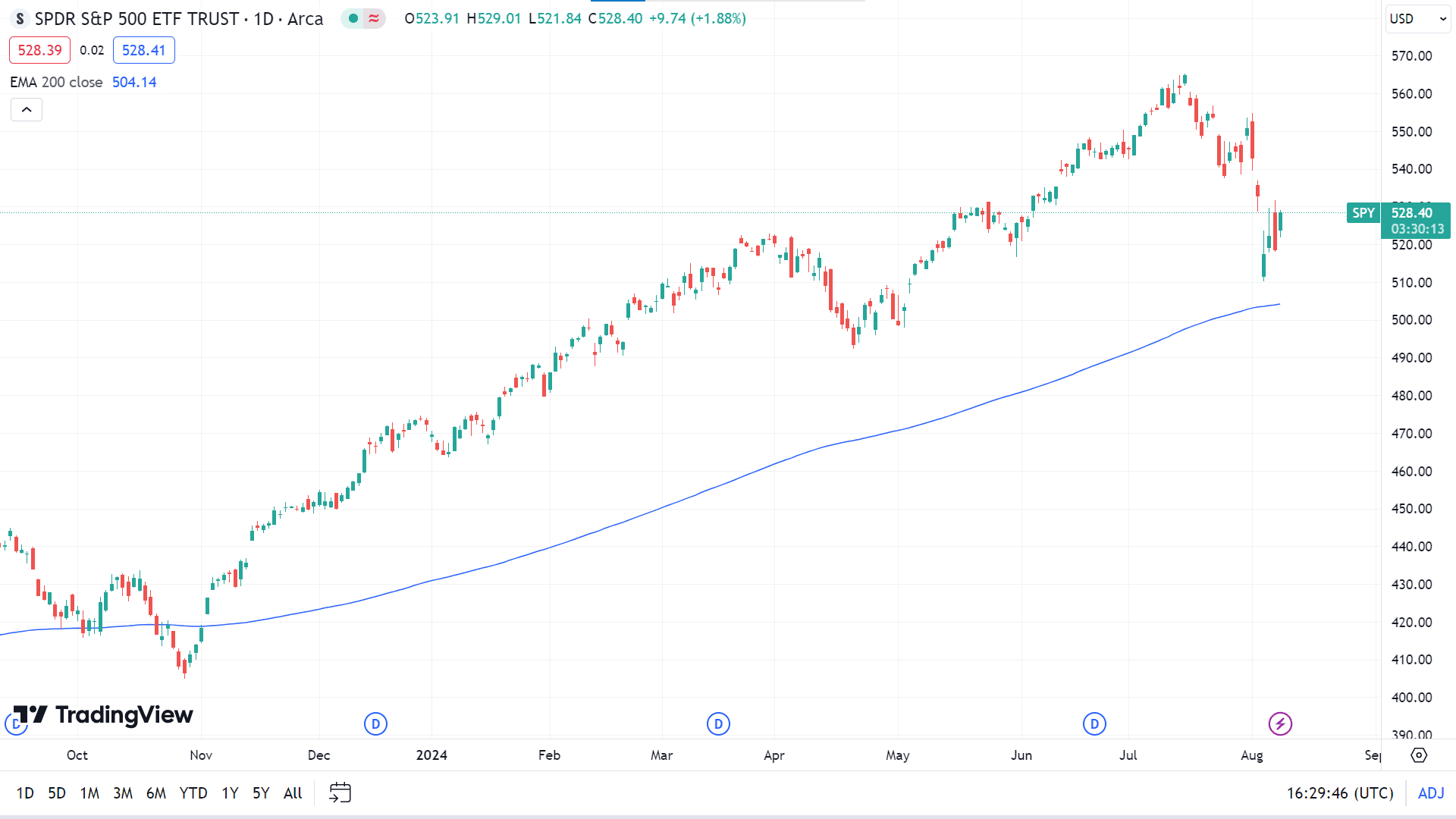
The asset SP500 ETF Trust (SPY) belongs to the large bend category and the fund family of SPDR State Street Global Advisors. The Trust strives to meet its investment objective by holding a portfolio of common stocks in the index. The weight of each stock in the Portfolio is carefully aligned with its corresponding weight in the index, ensuring the portfolio closely reflects the index’s composition.
Key Features
● Annual Report Expense Ratio (net) - 0.09%
● Net Assets - 562.5 B
● YTD Daily Total Return - 9.82%
● 1-Year Return - 16.69%
● PE Ratio (TTM) - 26.58
Pros And Cons
Pros of the SPY include,
● The SPY ETF provides exposure to 500 leading U.S. companies across various sectors, including 28% in information technology and 13.18% in healthcare.
● With a relatively low investment, such as $450, investors gain access to all 500 stocks in the S&P 500, benefiting from low transaction costs and high liquidity.
● The SPY ETF automatically matches the S&P 500's performance, removing the complex challenge of individually purchasing and weighing all 500 stocks.
Meanwhile, the Cons of SPY include,
● The S&P 500 trades at elevated price-to-sales and price-to-book ratios, near historical highs, raising concerns about overvaluation.
● The largest-weighted sector in SPY, Information Technology, may face significant challenges in 2022 due to high prices and valuation concerns.
● Rising interest rates and a high Shiller P/E ratio suggest a continued market selloff, which could negatively impact the S&P 500.
Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO)
Overview
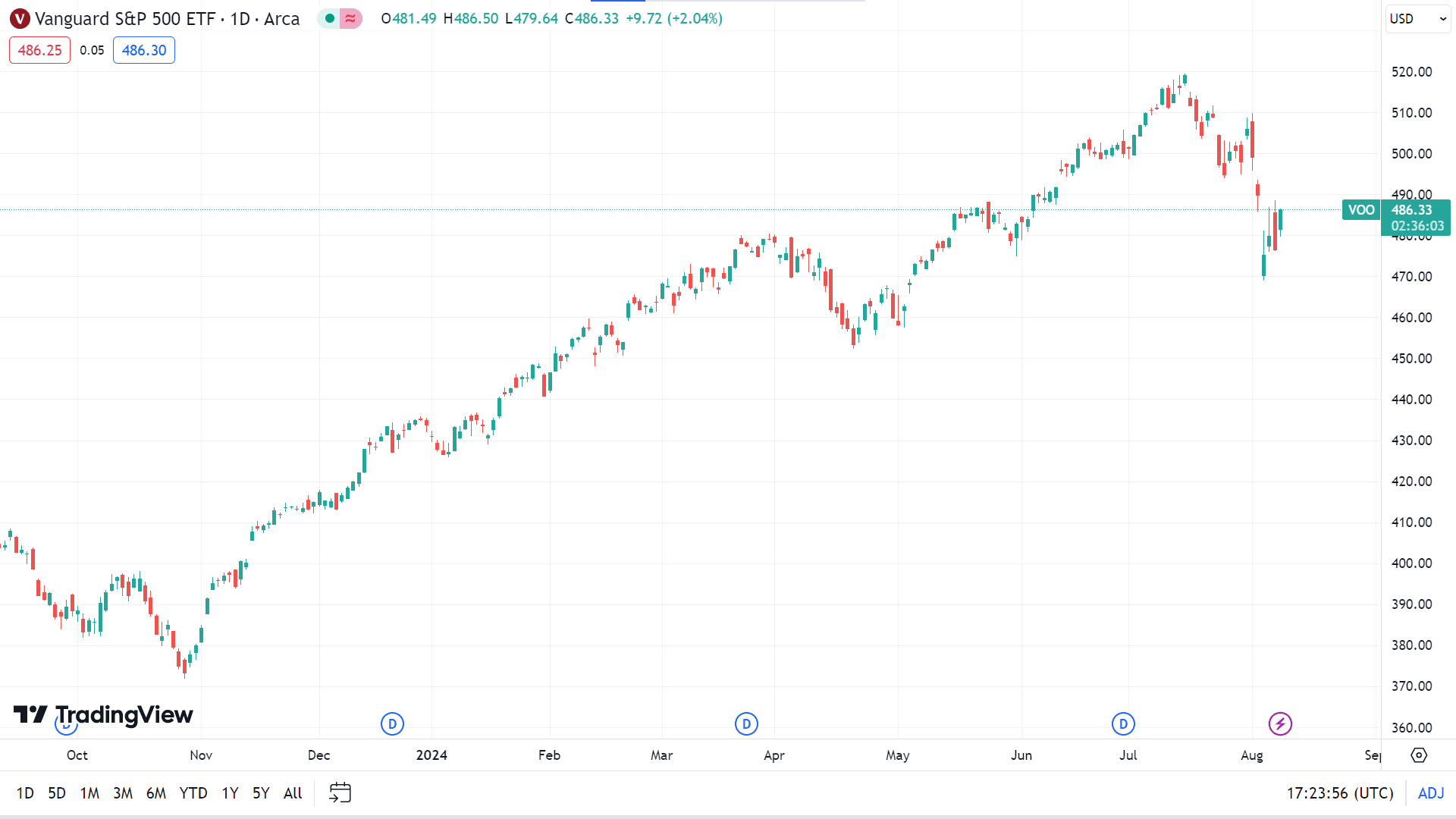
The Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO) is among the large bend category and belongs to the Vanguard fund family. The fund follows an indexing strategy to mirror the performance of the S&P 500, a key benchmark of large U.S. companies. It invests nearly all assets in the index's stocks, maintaining proportions aligned with its weighting. The fund is non-diversified. The inception date is 7 Sep 2010.
Key Features
● Annual Report Expense Ratio (net) - 0.03%
● Net Assets - 1.2 T
● YTD Daily Total Return - 9.86%
● 1-Year Return - 16.81%
● PE Ratio (TTM) - 26.44
Pros And Cons
The pros of the VOO include
● Instant diversification across 500 large U.S. stocks with close tracking of the S&P 500 Index.
● Extremely low expense ratio of 0.03%.
● High liquidity, making it one of the most heavily traded ETFs.
The cons of the VOO include
● Lacks exposure to mid and small-cap stocks, focusing solely on U.S. large-cap equities.
● No control over individual stock selections, limiting customization.
● Susceptible to American market downturns with minimal dividend yield.
iShares Core S&P 500 ETF (IVV)
Overview
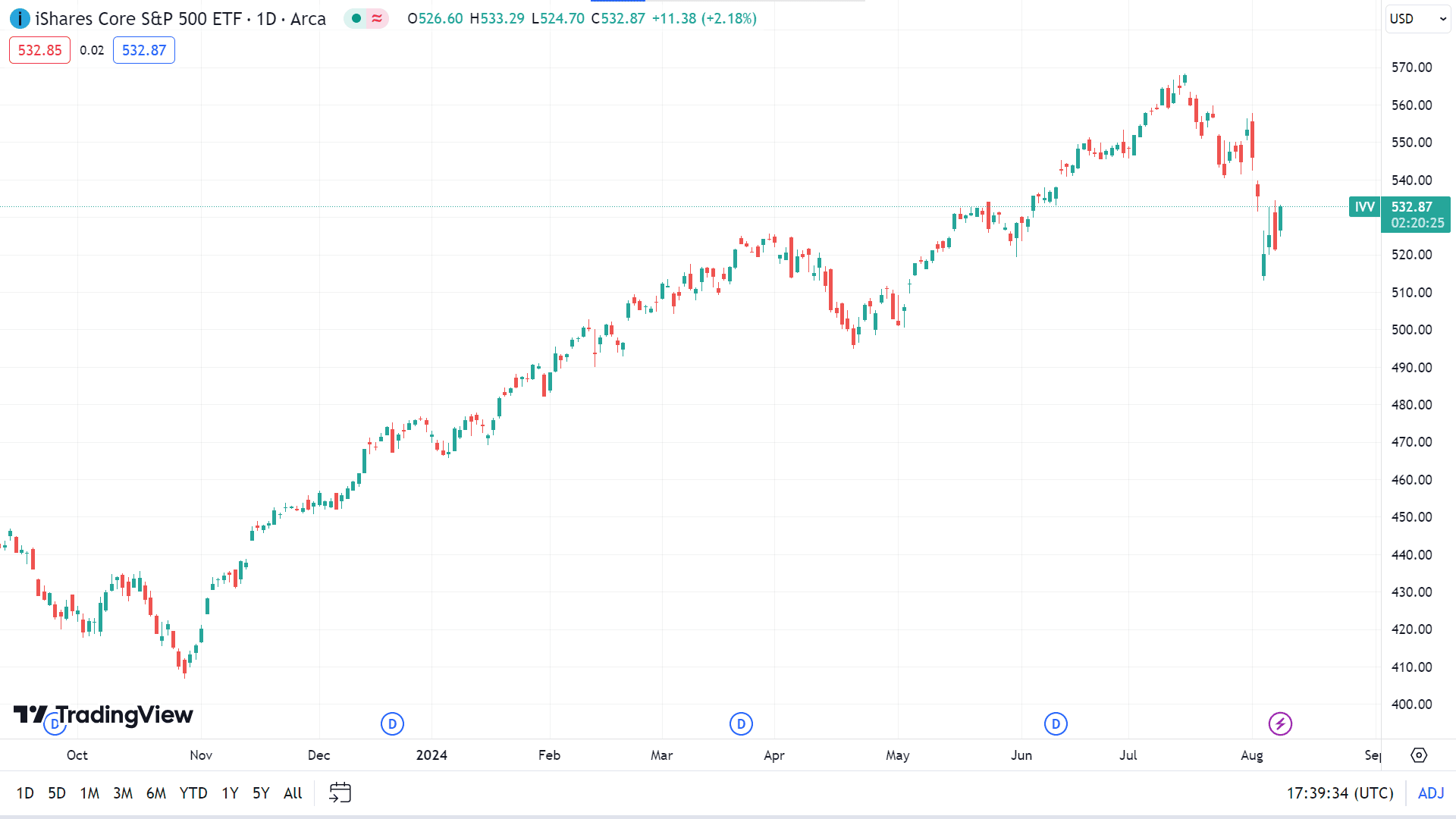 The inception date of the fund iShares Core S&P 500 ETF (IVV) is 15 May 2000. It is among the large bend category and belongs to the iShare fund family. The index captures U.S. large-cap performance, as defined by SPDJI. The fund invests at least 80% in index securities and similar assets and up to 20% in futures, options, swaps, and cash equivalents.
The inception date of the fund iShares Core S&P 500 ETF (IVV) is 15 May 2000. It is among the large bend category and belongs to the iShare fund family. The index captures U.S. large-cap performance, as defined by SPDJI. The fund invests at least 80% in index securities and similar assets and up to 20% in futures, options, swaps, and cash equivalents.
Key Features
● Annual Report Expense Ratio (net) - 0.03%
● Net Assets - 503.39 B
● YTD Daily Total Return - 9.86%
● 1-Year Return - 16.83%
● PE Ratio (TTM) - 26.73
Pros And Cons
Pros of the ETF fund IVV include
● Dollar-cost averaging is a proven strategy at the ETF fund IVV.
● IVV has long-term growth trends that have historically supported capital gains.
● The IVV ETF unit price will likely be significantly higher in a decade.
Cons of the IVV include
● With a 1.08% dividend yield, this ETF is better suited for capital growth rather than income generation.
● Historically elevated, the S&P 500’s P/E ratio of 34 raises valuation concerns.
● The index’s high P/E is influenced by its significant weighting in the technology sector, which typically commands higher valuations.
Schwab S&P 500 Index Fund (SWPPX)
Overview
 The inception date of the Schwab S&P 500 Index Fund (SWPPX) is 19 May 1997. The fund is among the large blend fund categories and belongs to the Schwab Funds fund family. The fund invests at least 80% of its net assets, often more, in the stocks of 500 leading U.S. companies, replicating the index by matching the weightings of each stock.
The inception date of the Schwab S&P 500 Index Fund (SWPPX) is 19 May 1997. The fund is among the large blend fund categories and belongs to the Schwab Funds fund family. The fund invests at least 80% of its net assets, often more, in the stocks of 500 leading U.S. companies, replicating the index by matching the weightings of each stock.
Key Features
● Annual Report Expense Ratio (net) - 0.02%
● Net Assets - 98.64 B
● YTD Daily Total Return - 16.66%
● 1-Year Return - 22.10%
Pros And Cons
Pros of the ETF fund SWPPX include
● The fund has a five-star rating from Morningstar.
● The expanse ratio is too low.
● The fund provides attractive returns over time.
Cons of the ETF fund SWPPX include
● WPPX offers a modest dividend yield, which may not satisfy income-seeking investors.
● Concentrated in large-cap U.S. stocks, the fund lacks diversification across mid and small-cap sectors.
● Tied closely to the S&P 500, the fund is vulnerable to U.S. market downturns.
Fidelity 500 Index Fund (FXAIX)
Overview
 The inception date of the fund Fidelity 500 Index Fund (FXAIX) is 4 May 2011. It is one of the large blend fund categories and belongs to the Fidelity Investment fund family. The fund invests at least 80% of its assets in S&P 500 Index stocks, representing U.S. large-cap equities, and earns additional income by lending securities.
The inception date of the fund Fidelity 500 Index Fund (FXAIX) is 4 May 2011. It is one of the large blend fund categories and belongs to the Fidelity Investment fund family. The fund invests at least 80% of its assets in S&P 500 Index stocks, representing U.S. large-cap equities, and earns additional income by lending securities.
Key Features
● Annual Report Expense Ratio (net) - 0.01%
● Net Assets - 568.29 B
● YTD Return - 16.68%
● 1-Year Return - 22.15%
● Last Dividend - 1.18
Pros And Cons
Pros of the ETF fund FXAIX include,
● The funny got a five-star rating from Morningstar.
● The expense ratio is too low.
● The fund posted attractive returns historically.
Cons of the ETF fund FXAIX include,
● FXAIX is subject to market volatility, affecting the value of its holdings.
● The fund may experience tracking errors, leading to returns that differ from the S&P 500 Index.
● Economic and political factors can negatively impact fund performance.
Performance Comparison
Historical Returns of Leading S&P 500 ETFs
Review the long-term performance of top S&P 500 ETFs to identify consistent growth patterns, providing insights into their historical strength and resilience.
Let’s see the 5 years growth for top S&P 500 ETFs:
|
Name |
Growth in 5 Years |
|
SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust (SPY) |
127.02% |
|
Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO) |
125.22% |
|
iShares Core S&P 500 ETF (IVV) |
127.65% |
|
Schwab S&P 500 Index Fund (SWPPX) |
118.3% |
|
Fidelity 500 Index Fund (FXAIX) |
125.06% |
Expense Ratios and Their Influence on Returns
Lower expense ratios can significantly enhance net returns over time. Even minor fee differences can substantially impact the long-term performance of these ETFs.
Let’s see the expense ratio for above-mentioned ETFs:
|
Name |
Expense ratio |
|
SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust (SPY) |
0.09% |
|
Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO) |
0.03% |
|
iShares Core S&P 500 ETF (IVV) |
0.03% |
|
Schwab S&P 500 Index Fund (SWPPX) |
0.02% |
|
Fidelity 500 Index Fund (FXAIX) |
0.02% |
Additional Performance Metrics
Evaluate key factors such as tracking error, dividend yield, and volatility to understand each ETF's performance relative to the S&P 500 Index and its competitors.
How to Invest in S&P 500 ETFs
ETFs trade similarly to stocks with a set share price. You might pay the full share price or buy fractional shares, depending on your broker. Like index funds, ETFs have expense ratios, so review the fees before investing. Before making investment decisions, check on factors like expense ratio, minimum investment amount, and dividend yields.
Steps to buying SP 500 ETFs
● Step One: In the first step, investors must select a traditional brokerage and sign up for trading SP500 ETFs. Where they can choose their desirable ETFs among many other available assets.
● Step Two: In the following step, investors must add funds to their brokerage accounts to invest in their desirable SP 500 ETFs.
● Step Three: Once investors decide on investments, they may purchase their selected asset through their brokerage account. Apply the key criteria mentioned earlier to compare dividend yields and expense ratios. This approach will help you evaluate how income distributions and fees influence the overall performance and appeal of each ETF.
Best platforms for ETF investing
Some best platforms to trade SP500 ETFs include,
● Charles Schwab
● Fidelity Investments
● Vanguard Group
● E-Trade Financial
● Firstrade
● Merrill Edge
● Ally Invest
Tips for maximizing returns
● Invest for the Long Term: Hold S&P 500 ETFs over an extended period to benefit from market growth and compounding.
● Minimize Fees: Select ETFs with low expense ratios to maximize net returns.
● Reinvest Dividends: Use dividend reinvestment plans to compound returns over time.
● Diversify Holdings: Consider balancing S&P 500 ETFs with other assets to manage risk and optimize returns.
Common Myths About S&P 500 ETFs
Myth 1: All SP500 ETFs are the same
Not all S&P 500 ETFs are identical. While they track the same index, differences can arise in expense ratios, tracking accuracy, and additional features. Over time, the ETF market has expanded to include specialized, factor-based, and actively managed options, offering varied investment strategies beyond standard S&P 500 exposure.
Myth 2: SP500 ETFs are only for beginners
Although S&P 500 ETFs are popular among beginners for their simplicity and broad market exposure, they are not limited to novice investors. Their ease of use and diversified exposure make them suitable for investors of all experience levels, offering a foundational investment option that can fit into various investment strategies.
Myth 3: High expense ratios mean better performance
A high expense ratio does not guarantee better performance. For instance, while equity ETFs generally have low expense ratios, averaging 0.16%, some equity mutual funds have even lower fees, below 0.10%. The ARK Innovation ETF (ARKK) has a higher expense ratio of 0.75%, which does not necessarily translate to superior performance compared to the average 0.47% expense ratio of stock mutual funds.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Real-life examples of successful S&P 500 ETF investors
Here are a few real-life examples of successful S&P 500 ETF investors:
Warren Buffett
In a 2013 letter to Berkshire Hathaway shareholders, Buffett stated that he had authorized the trustee of his estate to invest 90% of the money left to his wife in a low-cost S&P 500 ETF, with the remaining 10% in short-term government bonds. Buffett's faith in the S&P 500's long-term performance demonstrates the ETF's potential for consistent returns.
Jack Bogle
In 1976, Bogle launched the Vanguard 500 Index Fund, which aimed to track the performance of the S&P 500 index. Initially met with skepticism, the fund has since grown into one of the largest in the world, with trillions of dollars in assets under management.
The FIRE Movement
Many FIRE supporters have attained early retirement by disciplined saving and investing in low-cost index funds such as the S&P 500 ETF. Individuals who consistently invest considerable income in these funds have amassed substantial wealth over time.
Lessons Learned from Their Experiences
These success stories provide valuable lessons for investors considering the S&P 500 ETF:
Long-Term Focus
With its consistent growth over time, the S&P 500 exchange-traded fund (ETF) is an excellent choice for investors with a long-term investing horizon. Trying to time the market or looking for gains in the short term frequently results in less-than-desirable results. Instead, the most important thing is to invest patiently and consistently.
Diversification
The exchange-traded fund (ETF) that tracks the S&P 500 index provides exposure to various businesses and industries, offering a degree of diversification that helps reduce risk. By taking advantage of this broad exposure, investors can profit from the expansion of the United States economy rather than betting on specific stocks.
Implement of Compounding
Reinvesting dividends and allowing gains to compound over time is another critical factor in these investors' success. The power of compounding can lead to exponential growth in wealth, especially when combined with a long-term investment strategy.
Conclusion
According to the information presented in this article, exchange-traded funds (ETFs) provide the advantages of diversification, decreased risk, and the possibility for long-term growth, which makes them an essential component of many investment portfolios. Investors can make educated selections that align with their financial objectives if they are thoroughly aware of the aspects that influence the performance of exchange-traded funds (ETFs), such as fee ratios, tracking accuracy, and liquidity.
Before committing to S&P 500 exchange-traded funds (ETFs), it is essential to conduct exhaustive research and consider one's particular financial goals and how much risk one is willing to take. As a result of the fact that these funds provide a dependable way to take part in the expansion of the economy of the United States, they are an excellent addition to a comprehensive investment strategy.
Additional Resources
Below are some recommended resources to help you deepen your knowledge and make informed decisions:
1. Books
● The Little Book of Common Sense Investing by John C. Bogle: A classic guide on index investing, offering insights into the benefits of ETFs like SP500 ETFs.
● A Random Walk Down Wall Street by Burton G. Malkiel: Provides a comprehensive overview of different investment strategies, including the importance of diversification through index funds.
● The Intelligent Investor* by Benjamin Graham: A timeless read on value investing that complements an understanding of the role SP500 ETFs can play in a balanced portfolio.
2. Websites
● ETF.com: Offers detailed information on all ETFs, including SP500 ETFs, with articles, comparisons, and the latest news.
● Morningstar: A leading investment research platform providing in-depth analysis, performance metrics, and ratings for SP500 ETFs.
● Investopedia: A great resource for beginners and seasoned investors alike, with easy-to-understand articles on ETFs, index investing, and market trends.
*Disclaimer: The content of this article is for learning purposes only and does not represent the official position of SnowBallHare, nor can it be used as investment advice.